|
This post was edited by kr.AYAMAN at 18:47, Jun-24-2018 Greetings MIUIers, Hope you are well versed with smartphone displays.Smartphone display acronyms can be a little overwhelming, but if you want to know what all the numbers and abbreviations associated with smartphone screens mean, we've got you covered. Want to know what each screen type is best for and what the differences in screen resolution mean? Read on.
 One major consideration when we talk about smartphone screens can largely be boiled down to the resolution of the display, and as a rough guide, larger numbers are better here. Encompassed within this 'resolution' category is the size of the screen (in inches), the number of pixels (how much information it can show) and how densely those pixels are packed, referred to as Pixels Per Inch (ppi). If you know the size of the display, you can work out how many pixels are squeezed into one square inch: that's the pixels per inch (ppi) figure, which is referred to as pixel density. You can easily calculate your phone's ppi using a Pixel density calculator. Resolution explained
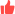
HD HD stands for high definition. HD simply means a pixel measurement of 1280 x 720 pixels. No matter how large the screen is, as long as the pixel measurement remains at this measurement, it's an HD display. As you can probably tell, the smaller the HD screen the higher the pixel density and, theoretically, the better the picture. So simply having an HD display doesn't mean much, as it will produce a very different image on a 5-inch screen form a 10-inch screen (note: screen sizes are measured on the diagonal to take account of slightly different aspect ratios). On a 4.3-inch screen, for example, the pixel density is 342 ppi. On a 4.7-inch screen, the pixel density drops to 312 ppi, but both are still HD displays. According to some companies, 300 ppi is the sweet spot, because that is roughly the point at which the human eye stops being able to discern individual pixels at a certain viewing distance (and on a certain sized screen). Full HD https://encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcSbDul0GZxAXxeZM4_O2eBWnGaHk99NQyLA43enJMGcYhhcl70e Full HD is the next step up and is currently the standard for smartphone display definition, although 2K (QHD) has been gaining traction on high-end devices. Full HD measures 1920 x 1080 pixels. Again, the pixel density will depend on how large the screen is overall. With smartphones at the 5-inch mark, the pixel density sits around 440 ppi, while on a 5.5-inch screen that number drops to 400 ppi. QHD (Quad HD) or 2K https://encrypted-tbn2.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcRzNkwxVUmMzRUylaG4stVK7KFKtKLwX-vND_Gqt0qg3-Pc5LSnTb2RAjI9 QHD stands for Quad HD, which is four times the definition of standard HD. That means you can fit the same number of pixels as four HD displays into a QHD display of the same size. The pixel measurement for QHD is 2560 x 1440 pixels. A 5.5-inch QHD display has a pixel density of 538 ppi. For comparison, the pixel density of a 5.5-inch Full HD screen is 400 ppi. Definitions are also often referred to by the smaller number of the pixel measurement, so HD will sometimes be called 720p, Full HD gets called 1080p and so on. With QHD though, the 2K name comes from the fact that the bigger of the pixel measurements is over 2000 pixels, which can admittedly be a bit confusing (and really ought to be referred to as 2.5K, if we were being entirely accurate). 4K or Ultra HD https://encrypted-tbn3.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcQvsfcxsEz7aM7aAK1tmes7Rv5B5k_5WCevvOdjQv9p3tik33aL7q6HORi0 You can probably see where this is going. Like 2K, the 4K name comes from the larger of the two pixel measurements, which are, technically speaking, 4096 pixels in 4K and only 3840 pixels in Ultra HD. So while these two terms are often used interchangeably, they are actually a little bit different. Ultra HD is 3860 x 2160 pixels and 4K is 4096 x 2160. Both definitions frequently get shortened to 2160p and the pixel difference is relatively marginal, but there is a difference.
There are many display types used in smartphones: LCD, OLED, AMOLED, Super AMOLED, TFT, IPS and a few others that are less frequently found on smartphones nowadays, like TFT-LCD. One of the most frequently found on mid-to-high range phones now is IPS-LCD. But what do these all mean? LCD LCD means Liquid Crystal Display, and its name refers to the array of liquid crystals illuminated by a backlight, and their ubiquity and relatively low-cost makes them a popular choice for smartphones and many other devices. LCDs also tend to perform quite well in direct sunlight, as the entire display is illuminated from behind, but does suffer from potentially less accurate color representation than displays that don't require a backlight. Within smartphones, you have both TFTand IPS displays. TFT stands for Thin Film Transistor, an advanced version of LCD that uses an active matrix (like the AM in AMOLED). Active matrix means that each pixel is attached to a transistor and capacitor individually. The main advantage of TFT is its relatively low production cost and increased contrast when compared to traditional LCDs. The disadvantage of TFT LCDs is higher energy demands than some other LCDs and less impressive viewing angles and color reproduction. Its for these reasons, and falling costs of alternative options, that TFTs are less regularly used in smartphones now. IPS stands for In-Plane Switching and it is a further improvement on TFT LCDs that delivers better color reproduction and, most notably, improved viewing angles than TFT-LCDs. It does this by using two transistors for each pixel combined with a more powerful backlight, but the downside is that they require more power than other types of non-LCD display. They generally use less power than a TFT display still though. There are other acronyms you many see combined with IPS too, like IPS-NEO. In that case, it's a proprietary name for a technology created by JDI that claims to eliminate backlight leakage, but it works in the same essential way as any other IPS-LCD display. AMOLED and OLED https://encrypted-tbn3.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcSv6gkPin1T8vjPf8CK-EvM2SyvbWjYwqvJyoGPSE_e_gHMSAmKk_gsz1ow AMOLED stands for Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode. While this may sound complicated it actually isn't. We already encountered the active matrix in TFT LCD technology, and OLED is simply a term for another thin-film display technology. OLED is an organic material that, like the name implies, emits light when a current is passed through it. As opposed to LCD panels, which are back-lit, OLED displays are 'always off' unless the individual pixels are electrified. This means that OLED displays have much purer blacks and consume less energy when black or darker colors are displayed on-screen. However, lighter-colored themes on AMOLED screens use considerably more power than an LCD using the same theme. OLED screens are also more expensive to produce than LCD. Because the black pixels are 'off' in an OLED display, the contrast ratios are also higher than LCD screens. AMOLED displays have a very fast refresh rate too, but on the down side are not quite as visible in direct sunlight as backlit LCDs. Screen burn-in and diode degradation (because they are organic) are other factors to consider. On the positive side, AMOLED screens can be made thinner than LCDs (because they don't require a backlit layer) and they can also be made flexible. Difference between OLED, AMOLED and Super AMOLED: OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode, and an OLED display is comprised of thin sheets electroluminescent material, the main benefit of which is they produce their own light, and so don't require a backlight, which cuts down on energy requirements. OLED displays are more commonly referred to as AMOLED displays when used on smartphones or TVs. As we've already covered, the AM part of AMOLED stands for Active Matrix, which is different again from a Passive Matrix OLED (P-OLED), though these are less common in smartphones. Like IPS LCDs, Super AMOLED improves upon the basic AMOLED premise by integrating the touch response layer into the display itself, rather than as an extra layer on top. As a result, Super AMOLED displays handle sunlight better than AMOLED displays and also require less power. As the name implies, Super AMOLED is simply a better version of AMOLED. Source: Android Image source: Google  Credits  Special Thanks to our admin @candicesu and all Devices Mods and Smods for their work and @choukawaii and @RlnzImpulse for guiding me. |
In order to fulfill the basic functions of our service, the user hereby agrees to allow Xiaomi to collect, process and use personal information which shall include but not be limited to written threads, pictures, comments, replies in the Xiaomi Community, and relevant data types listed in Xiaomi's Private Policy. By selecting "Agree", you agree to Xiaomi's Private Policy and Content Policy .
Agree

 Rate
Rate



 Get new
Get new